Aircraft and Aerospace NDT
Eddyfi Technologies for Aircraft and Spacecraft Inspection Applications
In an industry that designs components as lightweight as possible yet still able to perform critical functions, The aerospace sector needs the best of what non-destructive testing (NDT) has to offer.
Details
In an industry that designs components as lightweight as possible yet still able to perform critical functions, the aerospace sector needs the best of what non-destructive testing (NDT) has to offer. Comprised of jet engines/turbines, wings, propulsion tanks, fuselage, fasteners, friction stir welds, orbital welds, composites, and typically a lot of aluminum, both aircraft and spacecraft feature many crucial parts carrying high payloads relative to their material strength. Add the harsh operating conditions of extreme varied temperatures and low gravity, and this highlights the importance of detecting the smallest flaws early to prevent calamitous failure.

From the verification of new materials and the development of new vehicles to Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul (MRO) work, NDT is used for the entire lifecycle of aircraft and spacecraft. Many components are prone to fatigue cracking after being subjected to intense and near-continuous use, making preventative maintenance essential. Supervisory bodies oversee safety so that it reaches the highest possible levels, and several standards apply to the functional safety of aerospace vehicles. Maintenance protocols are exhaustive and time-consuming, especially when fuselage and engines are involved.

When it comes to crack detection, aerospace component inspection usually involves assessing parts made of aluminum alloy with complex geometry, boreholes of titanium components, multilayered aluminum structures, PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate also called acrylic glass) plates, T-section stiffeners, wing fasteners, longerons, jet engine fan blades, disks and blisks, and more. Cracks risk going undetected because they are small, near and under fastener heads for example, and often under surface coatings. Potential cracks existing in the vicinity of fasteners are short, they spread in all directions, and they are often subsurface, making them difficult to detect. Crack detection in T-section stiffeners is also a recurrent problem for aerospace manufacturers. In most cases, access to the stiffener is not easy and the complete top surface is not necessarily accessible.
Two different methods are often used to perform NDT inspections of aerospace assets.

Eddy Current Testing
Eddy current testing (ECT) is an electromagnetic technique perfectly suited to inspect non-ferromagnetic materials for near-surface and surface-breaking defects. It is widely used during both manufacturing and MRO work to detect fabrication flaws or fatigue-related defects such as cracking or corrosion found in multi-layered aluminum structures. An evolution of ECT, Eddy Current Array (ECA) is a major improvement as it allows covering a larger area in a single pass, making the examination less operator-dependent and less time consuming, while providing clear 2D/3D images of the part being tested.
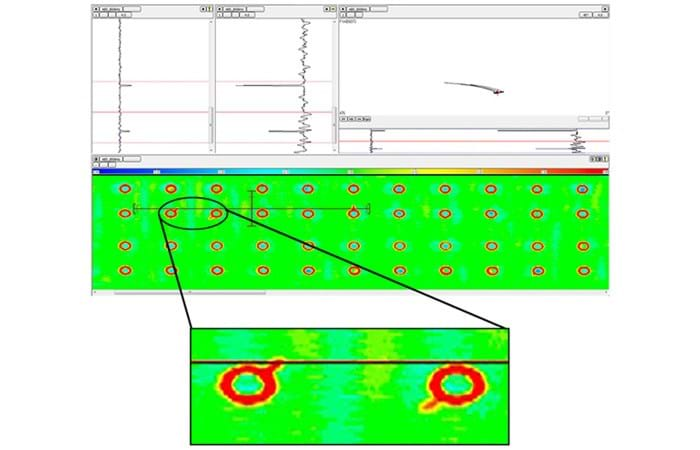
Eddyfi Technologies offers ECT and ECA solutions for the aerospace industry to help aircraft and spacecraft operators, component manufacturers such as jet engine makers and inspection companies comply with regulations. Our electromagnetic solutions help detect and characterize defects in commercial and military aircraft/spacecraft that other NDT technologies often have a hard time detecting. Typical applications include:
- Turbine and other jet engine components (e.g. cracking);
- Multilayered aluminum structures (e.g. corrosion at faying surfaces);
- Welds, such as Friction Stir Welds (FSW) or critical orbital welds;
- Defects under coatings and paint (without the need for scraping);
- Micro-cracking around fasteners on fuselage;
- Composite overwrapped pressure vessels (COPV).

Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT)
Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is a conventional inspection technique that has been used in the aerospace industry for decades. Unlike conventional UT, PAUT allows focusing and steering the ultrasonic beam electronically without moving the transducer. For maintenance, repair and overhaul work, portable systems such as the M2M Gekko® or the M2M Mantis™ are ideal: they offer the best of what PAUT has to offer in a compact and rugged format. For manufacturing applications in the aerospace industry, the M2M Panther™ is the instrument of choice, as it offers unparalleled performance and speed combining PAUT with the most complete set of Total Focusing Method (TFM) imaging techniques.
-©M2M-01.jpg?preset=details-img-fb)
PAUT and TFM are ideal to carry out a number of examinations for aerospace related assets, for example:
- Fastener hole inspection (without the need to remove the fastener);
- Ultra-fast corrosion inspection on fuselage;
- Landing gear inspection for fatigue cracking;
- Raw material verification for the aerospace manufacturing sector (e.g. thick aluminum plates);
- Aircraft composite structures (e.g., CFRP stringers, stiffeners);
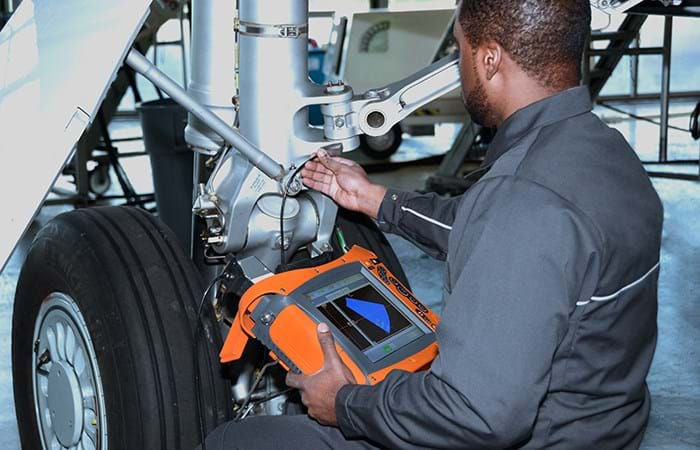

For the safety of all aerospace stakeholders, NDT is critical. Our range of solutions ensures the most advanced non-destructive testing for aircraft and spacecraft inspection applications.
